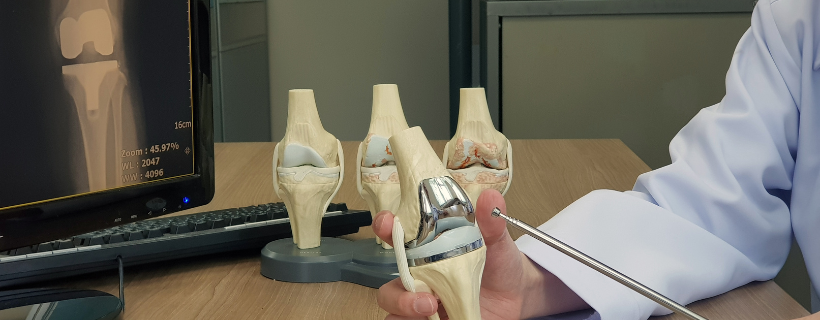
Total Knee Replacement Surgery (TKR), also known as Knee Arthroplasty or simply Knee Replacement, is a highly effective surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged or diseased knee joint with an artificial prosthesis. This procedure is commonly recommended for individuals suffering from severe knee pain caused by conditions like advanced arthritis, traumatic injuries, or other debilitating knee disorders that severely impact mobility and quality of life.
In a total knee replacement surgery, the surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone from the thighbone, shinbone, and kneecap. These are replaced with artificial components made from durable materials such as metal alloys, medical-grade plastics, and polymers. The goal is to restore joint function, alleviate pain, and allow patients to return to a more active and fulfilling lifestyle.
Common Conditions Leading to Total Knee Replacement Surgery
Several conditions can lead to the need for a knee replacement surgery. These include:
- Osteoarthritis – A prevalent degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis occurs mainly in middle-aged and elderly individuals. It involves the breakdown of cartilage and bone in the knee, causing stiffness, swelling, and pain.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis – This autoimmune condition leads to inflammation of the synovial membrane, which can damage the cartilage, causing pain, stiffness, and in some cases, joint deformity.
- Traumatic Arthritis – After an injury to the knee, trauma can lead to traumatic arthritis, which causes long-term knee pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion, eventually requiring a total knee replacement.
Why Should You Consider Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery might be the solution if you’re suffering from chronic knee pain that interferes with your daily life. Here are some reasons to consider:
- Pain Interfering with Daily Life – If you’re experiencing constant knee pain that disrupts your sleep, changes the way you walk, or makes daily activities like standing or climbing stairs difficult, a total knee replacement could provide lasting relief. If pain medications and other treatments have no longer worked, it might be time to consider surgery.
- A Safe and Common Procedure – Total knee replacement surgery is one of the most common and successful joint replacement surgeries performed globally. In countries like India, over 1,20,000 knee replacement surgeries are performed annually, with high success rates and patient satisfaction.
- Quick Recovery Time – After a total knee replacement, most patients are able to begin walking within 48 hours of surgery. With proper rehabilitation and physiotherapy, many individuals can walk without support within six weeks, returning to daily activities and even exercise.
- Additional Health Benefits – Beyond pain relief, a successful knee replacement allows you to stay more active, leading to:
- A lower risk of conditions like obesity, osteoporosis, and diabetes.
- Improved heart health and overall fitness.
- Better stability and a reduced risk of falls or further injuries.
Key Considerations Before Opting for Knee Replacement Surgery
Choosing to undergo total knee replacement surgery is an important decision. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Choose an Expert Surgeon: The success of your knee replacement surgery heavily depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon. It’s essential to select a highly qualified and experienced orthopedic surgeon who regularly performs joint replacements.
- Advanced Technology Matters: Computer-assisted navigation and other modern surgical tools can enhance the precision of the surgery. With better alignment, the results are often more successful, and the implants last longer.
- Comprehensive Post-Surgery Care: Rehabilitation and physiotherapy play a crucial role in a successful recovery. Choose a healthcare center that offers a comprehensive care approach, including tailored post-surgery rehabilitation programs to help you regain strength and mobility.
Conclusion
Is Knee Replacement Surgery Right for You?
Total knee replacement surgery is a highly effective and safe procedure for people suffering from severe knee pain due to conditions like arthritis or injury. By replacing a damaged joint with an artificial prosthesis, patients can experience reduced pain, increased mobility, and an overall improved quality of life.
When considering knee replacement surgery, make sure to consult with an experienced orthopedic surgeon, ensure the use of the latest surgical technologies, and follow a structured rehabilitation plan for the best results.
👉 If you are struggling with chronic knee pain and it’s affecting your lifestyle, total knee replacement surgery could be the solution to help you get back on your feet and enjoy a pain-free life again.
FAQs
1. What is Total Knee Replacement Surgery?
Total Knee Replacement Surgery (TKR) involves replacing a damaged knee joint with an artificial prosthesis to reduce pain and restore joint function.
2. Who is a candidate for Knee Replacement Surgery?
Candidates for knee replacement surgery include individuals with severe knee pain from arthritis, trauma, or degenerative diseases that interfere with daily activities.
3. What conditions require Total Knee Replacement?
Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and traumatic arthritis are common conditions that may lead to the need for total knee replacement surgery.
4. Is Total Knee Replacement Surgery safe?
Yes, total knee replacement surgery is generally safe and effective, with high success rates and low complication risks when performed by an experienced surgeon.
5. How long do knee replacement implants last?
Modern knee implants can last 15-20 years or longer, depending on the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health after knee replacement surgery.